

Igneous rocks are classified based on texture and composition. This relationship between cooling rates and grain sizes of the solidified minerals in igneous rocks is important for interpreting the rock’s geologic history. These are known as coarse-grained intrusive, or plutonic, igneous rocks. In contrast, magma that cools slowly below the earth’s surface forms larger crystals which can be seen with the naked eye. Half Dome, a mass of intrusive igneous rock in Yosemite National Park, now exposed by erosion.
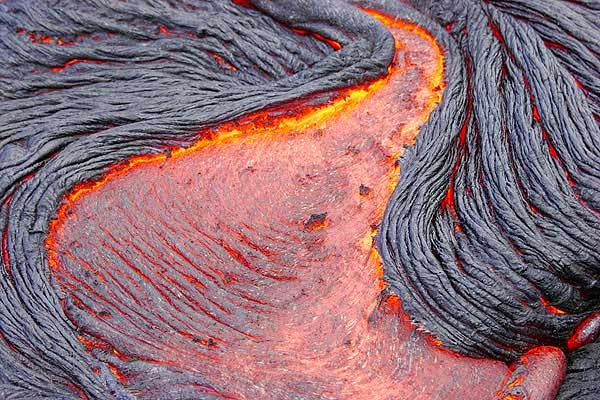

This leads to different types of volcanoes and different volcanic hazards. Depending on the properties of the lava that is erupted, the volcanism can be drastically different, from smooth and gentle to dangerous and explosive. Volcanism is the process in which lava is erupted. Extrusive rocks are often vesicular, filled with holes from escaping gas bubbles. These are known as fine-grained extrusive, or volcanic, igneous rocks. Lava flow in Hawaii Lava cools quickly on the surface of the earth and forms tiny microscopic crystals. This chapter will describe the classification of igneous rocks, the unique processes that form magmas, types of volcanoes and volcanic processes, volcanic hazards, and igneous landforms. It is this magma that becomes the source for volcanoes and igneous rocks. However, there are a few minor pockets of magma that form near the surface where geologic processes cause melting. Only the Earth’s outer core is liquid the Earth’s mantle and crust is naturally solid. This molten material is called magma when it is in the ground and lava when it is on the surface. Igneous rock is formed when liquid rock freezes into a solid rock. Describe volcano types, eruptive styles, composition, and their plate tectonic settings.
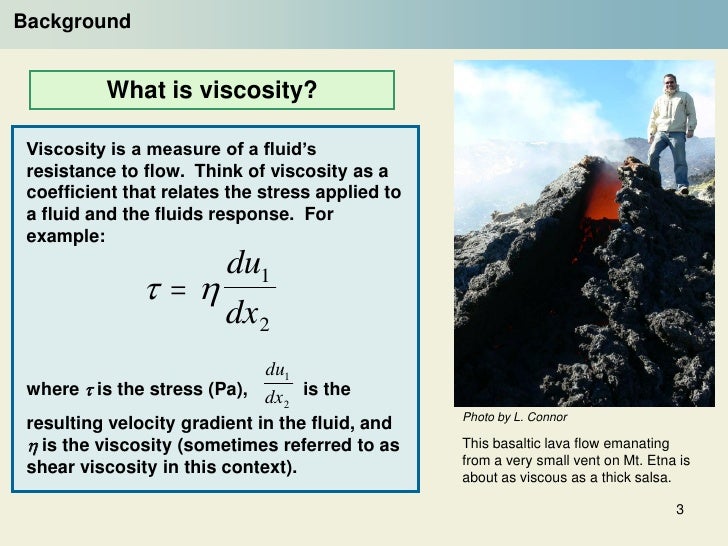
Describe how silica content affects magma viscosity and eruptive style of volcanoes.Explain partial melting and fractionation, and how they change magma compositions.Analyze the features of common igneous landforms and how they relate to their origin.Explain how cooling of magma leads to rock compositions and textures, and how these are used to classify igneous rocks.
#High viscosity magma series
Describe how the Bowen’s Reaction Series relates mineral crystallization and melting temperatures.Explain the origin of magma it relates to plate tectonics.4 Igneous Processes and Volcanoesīy the end of this chapter, students should be able to: Mount Vesuvius towers over the ruins of Pompeii, a city destroyed by the eruption in 79 CE.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
